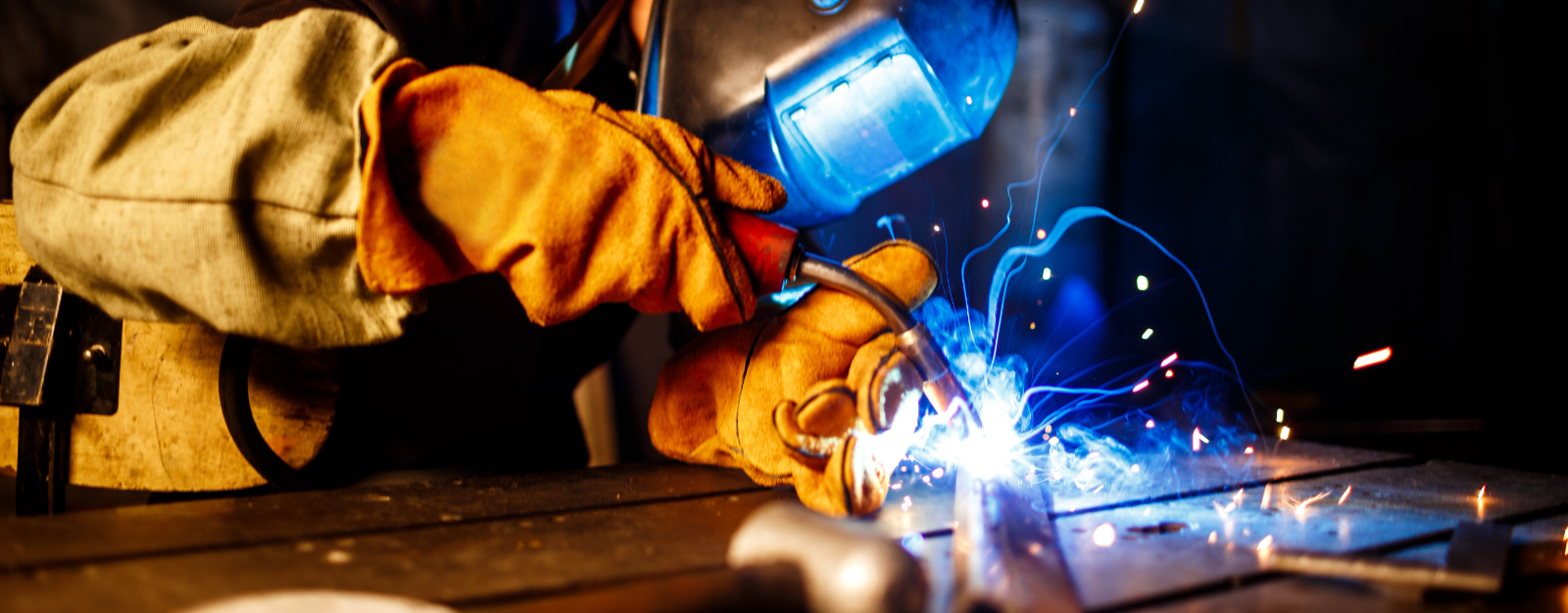
We discuss what equipment is needed for MIG welding. Explore expert recommendations and tips to ensure your MIG welding projects are precise, efficient, and safe.
What are the benefits of MIG welding?
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, is a popular form of welding employed across various sectors such as construction, automotive and more. As with any technology, it comes with its unique pros and cons.
MIG welding comes with numerous benefits. Firstly, learning MIG welding is extraordinarily straightforward and fast compared to other welding methods. This is largely due to its unique feature of automatic wire feeding, which minimises the demand for extensive manual control.
Also, it has better speed and productivity, making it perfect for industrial applications. Time and effort spent become considerably lower, contributing to increased efficiency. So overall, MIG welding tends to be efficient, user-friendly and can yield high-quality results.
Additionally, MIG welding produces cleaner results with less leftover waste material (slag), implying it's a more visually appealing method for welding. Its versatility is commendable, given it's adaptability to weld an extensive variety of metals along with different levels of thickness.
However, no technology is without its drawbacks. For MIG welding, the need for a shielding gas can be a disadvantage. The requirement for a continuous supply of gas means it isn’t usually suitable for use in outdoor conditions where the wind can disperse the gas. Also, MIG welding may not be the best option for thicker materials as it may not penetrate as deeply as other methods.
What’s The Difference Between MIG And TIG Welding?
MIG and TIG are two popular forms of welding, each with their unique merits and demerits. The key differences between these two lie primarily within their level of control, ease of learning and suitability for beginners.
TIG welding, also known as Tungsten Inert Gas welding, is a process often used by experienced craftsmen due to the superior control and precision it offers. This is particularly beneficial when working with thin metals as it allows for more delicate, detailed work. On the flip side, MIG welding, sometimes referred to as Metal Inert Gas welding, is generally considered the simplest welding method to master.
As such, it's often the first technique learned by novices. Its straightforward nature makes it accessible and less intimidating for beginners, allowing them to gain confidence quickly. Both TIG and MIG welding have their unique characteristics and benefits, and the choice between them often depends on the complexity of the task at hand, user's skill level, and the specific requirements of the project.

MIG welding is a popular method in the industry due to its automatic wire feed feature. This unique characteristic eliminates some of the manual elements of the process, making it a lot more user-friendly, particularly for novices learning the technique.
The automatic system also improves efficiency as it constantly feeds the wire, significantly increasing the speed of the welding compared to TIG welding, that involves more manual manipulation.
This means that MIG welding can often lead to faster project completion times, which is a definite advantage in a busy production environment. Therefore, choosing MIG welding can be a smart, time-saving choice for both beginners and professionals.
MIG welding, also known as Metal Inert Gas welding, is a superior method for novices, thanks to its user-friendly features. It stands out prominently due to the automatic wire feed mechanism that comes with it - a feature that remarkably lessens the skill intensity required. Contrary to this, in TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, the process is a bit more complicated.
In TIG, the welder needs to exhibit more finesse and coordination as the filler metal needs to be manually fed during the entire welding process, thereby making it more demanding and difficult for beginners.
However, both MIG and TIG have their own distinct advantages depending on the welding job at hand, the materials involved, and the desired finish. For beginners eager to embrace welding, understanding these differences can drastically improve their learning curve and mastery of the craft.
What tools are needed for MIG welding?
To begin, the cardinal gadget that is needed for MIG welding is the MIG welder. This is an accurate contraption that mechanically feeds a cable welding electrode into a handheld gun. The machine delivers the heat and energy for welding, and it's this heat that helps to fuse two pieces of metal together.
For the MIG welder to function adequately, it relies on a consistent and stable power source-- whether that's an electrical plug or a generator, without which it simply won't work.
Another prominent component of the MIG welding setup is the shielding gas. The primary objective of this gas is to preserve the integrity of the weld. It wraps the weld pool with a protective screen, guarding it against atmospheric gases, such as oxygen and nitrogen, that could cause contamination and subsequently compromise the quality of the weld.
On top of these, there are important safety gears that are paramount when MIG welding. These include welding gloves to protect your hands from burns and splatter, safety glasses to shield your eyes from intense light and debris, a welding helmet to protect your face and especially your eyes from the harmful ultraviolet and infrared light, and an apron to protect your clothing and body.
Welding is not a task to be taken lightly, and every single piece of safety equipment serves an essential purpose in preventing injury. Safety is always first, after all.
What gas is used for MIG welding?
The type of shielding gas you select in your MIG welding projects can significantly impact the final result. Two key gases typically used for this are Argon and Carbon Dioxide (CO2). Which of these to utilise primarily depends on the specific metal you are working with.

Argon, being a noble gas, has less reactivity than other gases with various elements. It is often the gas of choice when dealing with non-ferrous metals such as aluminium, copper, or brass.
This preference rises from the fact that pure Argon ensures a stable arc, reduced spatter, and reliable cleaning action, crucial attributes when welding these metal types. This promotes the purity of the weld, guaranteeing a clean and sturdy outcome.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2), conversely, is frequently chosen for welding steel, whether it's stainless, mild or carbon steel. CO2, more reactive than Argon, can result in a hotter, more deeply penetrating arc. This allows for more intense penetration into the metal, making it a perfect fit for thick, heavy-duty welds.
Often, you can achieve the best outcome by using a blend of both Argon and CO2. By carefully adjusting the ratio of these gases, you can enhance the arc's stability, spatter and penetration to best match your welding project's specifics. This allows you to benefit from both gases' advantages, contributing to a superior quality weld.
However, identifying the perfect blend of gases is a complex task. It involves consideration of the workpiece's nature, thickness, positioning, and the desired properties of the weld. If you're unsure which shielding gas to use for your welding endeavour, there are many professional welders you can call that are more than equipped to guide you. With our wealth of experience, we can assist you in selecting the optimal choice. Prioritise the quality of your welds by making the right selection of shielding gas.
How to Set Up to MIG Weld
Now that you're familiar with the basics of what equipment is needed for MIG welding, let’s delve a bit into the setup procedure. Here are the steps:
- Connect the MIG welder to a power source.
- Select the appropriate wire and install it in the welder.
- Install and connect the shielding gas.
- Set the wire feed speed and voltage on the welder based on the thickness and type of the metal.
- Put on your safety gear.
- Ensure the area is well ventilated.
- Start welding.
Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you weld, the better you will get at it. Happy welding!
Are you looking for welding equipment suppliers in Coventry and Warwickshire. Contact our welding equipment specialists working across Coventry, Rugby, Oxford and the surrounding areas.


